The ethereal dance of the Aurora Borealis, also known as the Northern Lights, has captivated humanity for centuries. Tonight, under the right conditions, you might witness this stunning spectacle firsthand. A confluence of solar activity and favorable atmospheric conditions are aligning, creating an exceptional opportunity to see the Northern Lights. Predicting the aurora's visibility is a complex science, but understanding the key factors can significantly increase your chances of experiencing this natural wonder.
Understanding the Aurora Borealis
The Aurora Borealis is a luminous atmospheric phenomenon predominantly observed in the high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). These mesmerizing displays of light, often appearing as shimmering curtains, rays, or diffuse glows, are caused by interactions between charged particles from the sun and the Earth's magnetic field. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) send streams of these charged particles hurtling toward Earth. When these particles collide with atoms and molecules in the Earth's upper atmosphere, they excite those atoms, causing them to release energy in the form of light. The color of the aurora depends on the type of atom or molecule that is excited and the altitude at which the collision occurs. Oxygen, for example, produces green and red light, while nitrogen produces blue and purple light.
Factors Influencing Aurora Visibility
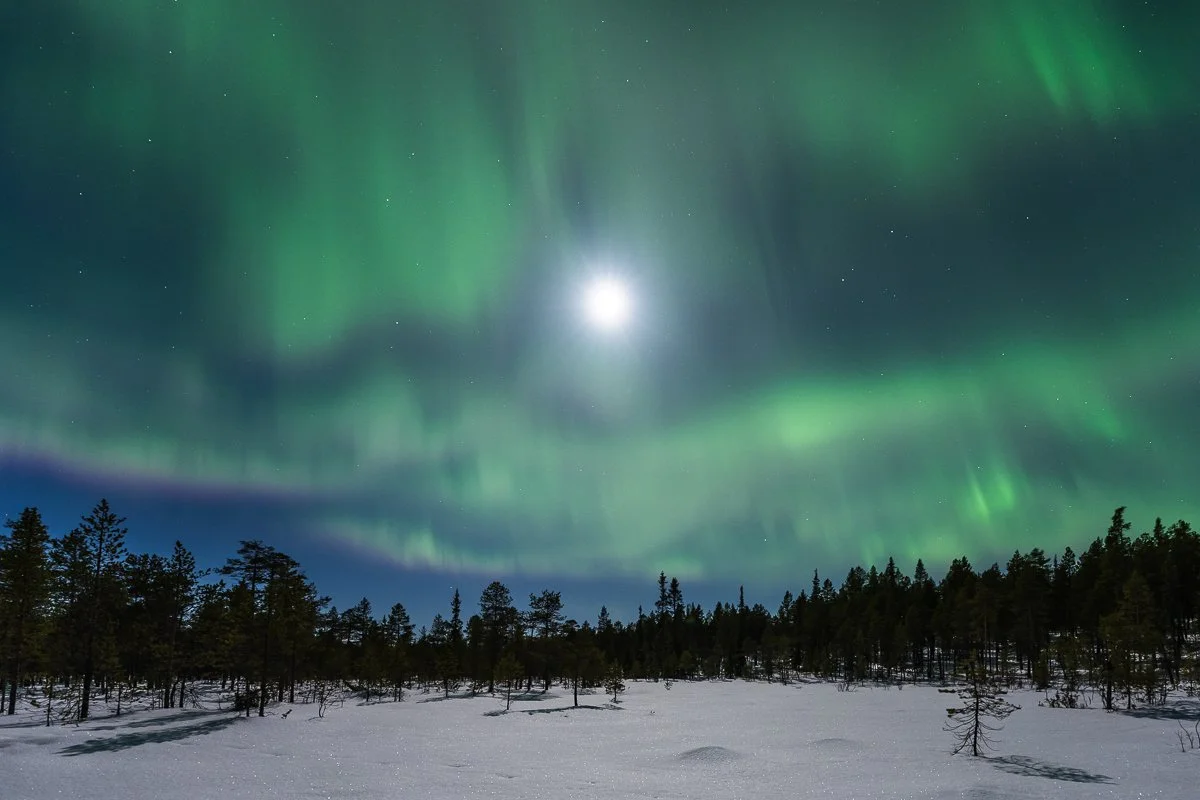

Several key factors influence the visibility of the Aurora Borealis. These include solar activity, geomagnetic activity, and local weather conditions. Solar activity, as measured by sunspot numbers and the frequency of solar flares, plays a crucial role. Higher solar activity generally translates to a greater chance of auroral displays. Geomagnetic activity, often measured by the Kp index, indicates the level of disturbance in the Earth's magnetic field. A higher Kp index signifies a stronger geomagnetic storm, which can push the aurora further south than usual. Local weather conditions, such as clear skies and minimal light pollution, are also essential for optimal viewing. Clouds can obscure the aurora, and artificial lights can diminish its visibility.
Tonight's Aurora Forecast

Tonight's aurora forecast is promising due to a combination of favorable factors. Recent solar activity has been elevated, with several solar flares and CMEs detected. These events have increased the likelihood of geomagnetic storms that could enhance auroral activity. Forecasters are predicting a moderate to strong geomagnetic storm, potentially reaching a Kp index of 5 or higher. This level of geomagnetic activity could make the aurora visible in areas further south than usual, including some mid-latitude locations. However, it's important to remember that aurora forecasts are inherently uncertain, and the actual intensity and extent of the display may vary. It is essential to check near-real-time space weather information from reliable sources.
Best Locations for Viewing
For those eager to witness the Northern Lights tonight, choosing the right location is paramount. Ideally, you want to be in an area with dark skies, away from city lights. Rural areas and remote wilderness locations are typically the best choices. Higher latitude regions, such as Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and Iceland, offer the most consistent opportunities for aurora viewing. However, with a strong geomagnetic storm, the aurora may be visible from lower latitudes, including parts of the northern United States, such as Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota. Consult light pollution maps to identify areas with minimal artificial light. Remember that patience is key; the aurora can be unpredictable, and it may take some time to appear.
Tips for Aurora Hunting

Hunting for the Aurora Borealis can be an exciting adventure. Here are some helpful tips to maximize your chances of success:
-
Check the Aurora Forecast Regularly: Stay updated on the latest aurora forecasts from reputable sources like the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) and local weather agencies. These forecasts provide information on solar activity, geomagnetic activity, and predicted aurora visibility zones.
- It's crucial to monitor real-time data because conditions can change rapidly.
-
Find a Dark Location: Escape the city lights and head to a dark, rural area. Use light pollution maps to identify areas with minimal artificial light. The darker the sky, the brighter the aurora will appear.
- Consider driving a bit further to get away from light pollution.
-
Dress Warmly: Aurora hunting often involves spending long periods outdoors in cold temperatures. Dress in layers, including a warm hat, gloves, scarf, and insulated boots.
- Consider bringing hand and foot warmers for extra comfort.
-
Bring a Camera: Capture the beauty of the aurora with a camera. A DSLR or mirrorless camera with a wide-angle lens is ideal for capturing the entire display.
- Use a tripod to keep your camera steady and prevent blurry images. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for capturing the light.
-
Be Patient: The aurora can be unpredictable. It may take some time for the display to appear, and the intensity can vary. Be patient and enjoy the beauty of the night sky while you wait.
- Consider bringing a book or listening to music to pass the time.
-
Use Aurora Viewing Apps: Several mobile apps provide real-time aurora forecasts, location finders, and other helpful information. Some popular apps include Aurora Forecast, My Aurora Forecast, and SpaceWeatherLive.
- These apps can help you find the best locations and predict when the aurora is likely to appear.
-
Minimize Screen Time: Avoid looking at your phone or other electronic devices for extended periods, as the bright light can affect your night vision.
- If you need to use your phone, dim the screen or use a red light filter.
Understanding Aurora Colors
The colors of the Aurora Borealis are determined by the type of gas molecules in the atmosphere that are excited by the charged particles from the sun. The most common color is green, which is produced by oxygen molecules at lower altitudes. Red aurora is produced by oxygen at higher altitudes. Blue and purple aurora are produced by nitrogen molecules. The intensity and mixture of colors can vary depending on the energy and density of the charged particles.
Capturing the Aurora with Photography

Photographing the Aurora Borealis can be a rewarding experience. Here are some tips for capturing stunning aurora photos:
-
Use a Wide-Angle Lens: A wide-angle lens (e.g., 14mm, 24mm) is ideal for capturing the vastness of the aurora display.
-
Use a Tripod: A tripod is essential for keeping your camera steady during long exposures.
-
Set a Wide Aperture: Use a wide aperture (e.g., f/2.8, f/4) to let in as much light as possible.
-
Use a High ISO: Increase the ISO to capture more light, but be mindful of noise. Experiment with different ISO settings to find the optimal balance between brightness and image quality.
-
Use Manual Focus: Autofocus may not work well in the dark. Use manual focus and focus on a bright star or distant object.
-
Experiment with Exposure Times: Experiment with different exposure times to find what works best for capturing the aurora. Start with a few seconds and adjust as needed.
-
Shoot in RAW Format: Shooting in RAW format allows you to make more adjustments to the image in post-processing.
The Science Behind Aurora Prediction
Aurora prediction is a complex science that involves monitoring solar activity, geomagnetic activity, and atmospheric conditions. Scientists use a variety of instruments, including satellites and ground-based observatories, to collect data on the sun and the Earth's magnetosphere. This data is used to develop models that can predict the likelihood and intensity of auroral displays. However, these models are not perfect, and there is still a degree of uncertainty in aurora predictions. Researchers are constantly working to improve these models and better understand the complex processes that drive the aurora.
Aurora Folklore and Mythology

The Aurora Borealis has been the subject of folklore and mythology for centuries. In many cultures, the aurora was seen as a sign of good fortune or a message from the gods. The Inuit believed that the aurora was the spirits of their ancestors playing ball in the sky. In Scandinavia, the aurora was associated with the Valkyries, female figures who escorted fallen warriors to Valhalla. These stories reflect the awe and wonder that the aurora has inspired in people throughout history.
Enjoying the Show Responsibly
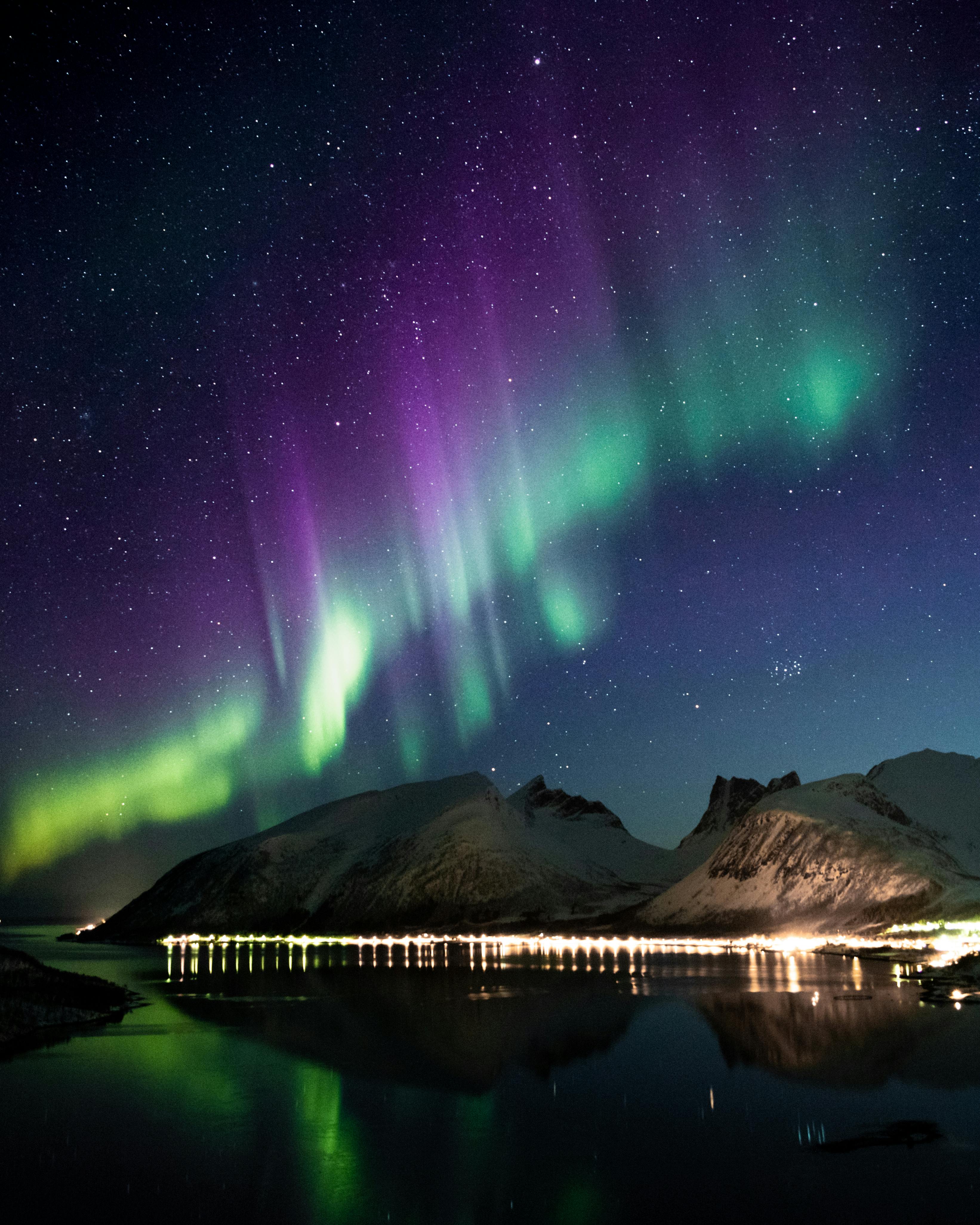

While chasing the aurora, it's important to be respectful of the environment and local communities. Avoid trespassing on private property, and be mindful of noise levels. Pack out all trash and leave no trace behind. If you're driving, be aware of wildlife and drive safely. Consider supporting local businesses and tour operators who offer responsible aurora viewing experiences. By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that future generations can enjoy the beauty of the Northern Lights.
The Aurora Borealis is a truly awe-inspiring natural phenomenon. Tonight, with a bit of luck and careful planning, you may have the chance to witness this magical display firsthand. Embrace the opportunity to connect with nature, learn about the science behind the aurora, and appreciate the beauty of the night sky.



No comments:
Post a Comment